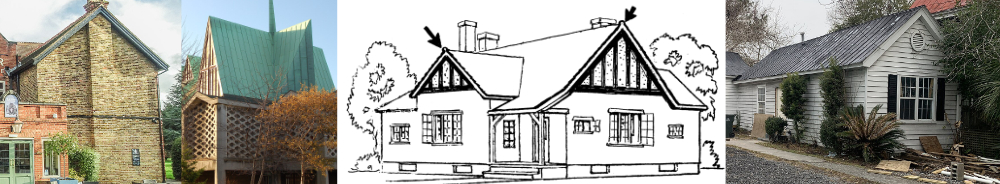
Gable roof
A gable roof, might be considered one of the most standard kinds of roof, where two halves of the roof meet at the highest point in a centre line, pitching down to an overhang on the side walls. The stright sides are closed up to the pitch by the gable, gable walls or gable ends which form an upper triangle enclosing the roof space.
Traditionally gable roofs were often cold timber roofs with the rafters laid at an angle, cut in at the top with bird mouth notches to sit on the ridge beam at the highest point, and tied together at the bottom with perpendicular tie beams. All parts working together structurally to form trusses, with the space above the tie beams being the vented cold roof space, usually vented at the eaves (where the joint of the rafters and tie beams sit on the supporting walls) and the space below being the warm insulated space, often with insultation between and above the tie beams. Other additions to the trusses to increase strength of efficiency might include king posts, queen posts and purlins, forming different types of trusses, roof formed of trusses that include purlins might also be called purlin rooves.
Other specific descriptions of a gable roof might include front gable, side gable and cross gable. A side or front gable simple describes where the gable end is in relation to the street, at the front or entrance to the house or at the side, with the pitch roof coming to the front. A cross gable roof is where two or more building blocks, with roof gable meet perpendicular to one another, thus creating a valley roof at the point where the two pitches meet and run into a valley gutter.
There are also other varieties of what might be called a gable roof, such as the Dutch gable and the box gable. The dutch gable being a hybrid between a hip roof and a gable roof, where the primarily hip roof has a gable roof at its uppermost point. The box gable is a standard gable, with the difference being at the gable ends, where the gable at the roof height protrudes from the wall below the gable end, so the gable ends overhang the wall as such.
For other related articles see types of roof, domestic roofs and types of truss.
See also: Gable and inverted gable.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
How can digital twins boost profitability within construction?
A brief description of a smart construction dashboard, collecting as-built data, as a s site changes forming an accurate digital twin.
Unlocking surplus public defence land and more to speed up the delivery of housing.
The Planning and Infrastructure bill oulined
With reactions from IHBC and others on its potential impacts.
Farnborough College Unveils its Half-house for Sustainable Construction Training.
Spring Statement 2025 with reactions from industry
Confirming previously announced funding, and welfare changes amid adjusted growth forecast.
Scottish Government responds to Grenfell report
As fund for unsafe cladding assessments is launched.
CLC and BSR process map for HRB approvals
One of the initial outputs of their weekly BSR meetings.
Architects Academy at an insulation manufacturing facility
Programme of technical engagement for aspiring designers.
Building Safety Levy technical consultation response
Details of the planned levy now due in 2026.
Great British Energy install solar on school and NHS sites
200 schools and 200 NHS sites to get solar systems, as first project of the newly formed government initiative.
600 million for 60,000 more skilled construction workers
Announced by Treasury ahead of the Spring Statement.
The restoration of the novelist’s birthplace in Eastwood.
Life Critical Fire Safety External Wall System LCFS EWS
Breaking down what is meant by this now often used term.
PAC report on the Remediation of Dangerous Cladding
Recommendations on workforce, transparency, support, insurance, funding, fraud and mismanagement.
New towns, expanded settlements and housing delivery
Modular inquiry asks if new towns and expanded settlements are an effective means of delivering housing.
Building Engineering Business Survey Q1 2025
Survey shows growth remains flat as skill shortages and volatile pricing persist.